Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has reshaped the world, driving innovation across industries such as healthcare, finance, and technology.. But how did AI develop over time? Understanding the artificial intelligence background helps us see how this technology evolved from simple automation to complex neural networks.
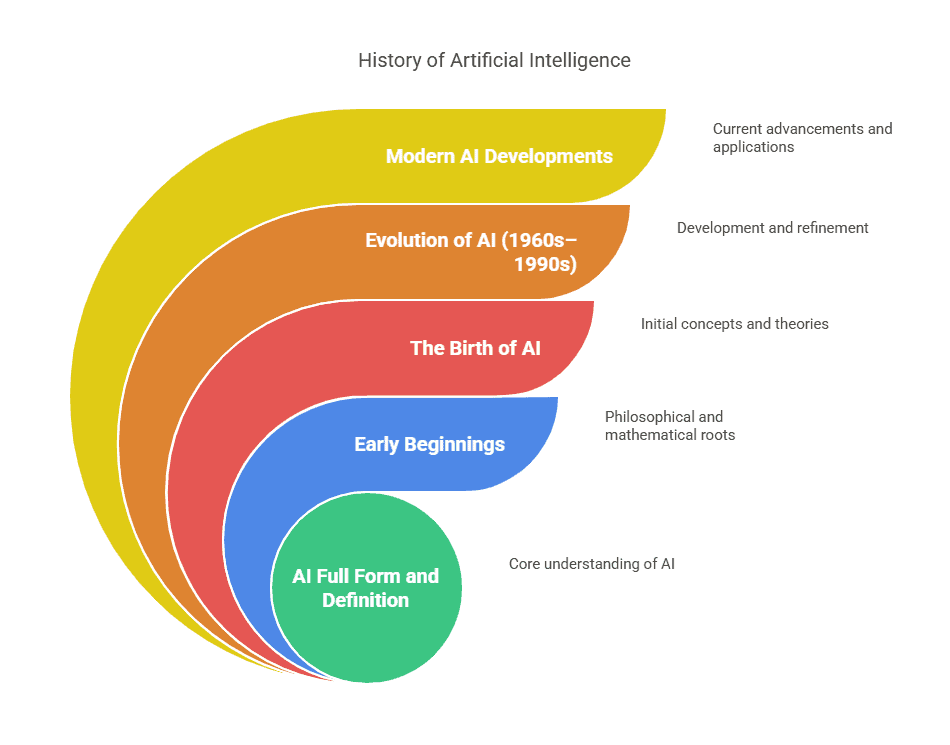
1. AI Full Form and Definition
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is the replication of human intelligence in machines. These systems can learn, solve problems, make decisions, and process language.
2. Early Beginnings: The Philosophical and Mathematical Foundations
The origin of AI can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where myths and mechanical inventions hinted at the possibility of intelligent machines. Key early developments include:
- Greek Mythology – Stories of automatons created by Hephaestus.
- Mathematical Logic (1600s-1800s) – Gottfried Leibniz and George Boole laid the groundwork for logical reasoning in machines.
- Alan Turing’s Turing Machine (1936) – Theoretical model proving that a machine could compute anything given the right algorithm.
3. The Birth of AI: Who Created AI? (1950s)
The official birth of AI as a field began in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where key scientists established AI as a distinct research area.
- Who invented artificial intelligence? The term “artificial intelligence” was coined by John McCarthy, an American computer scientist.
- Who invented AI? AI research was pioneered by McCarthy, along with Alan Turing, Marvin Minsky, Herbert Simon, and Claude Shannon.
- Early AI programs like Logic Theorist (1955) and General Problem Solver (1957) laid the foundation for modern AI.
4. The Evolution of AI (1960s–1990s): Growth and Challenges
During this period, AI saw both breakthroughs and setbacks:
- 1960s – First AI chatbots like ELIZA were created.
- 1970s–1980s – AI faced an “AI winter” due to lack of progress and funding.
- 1990s – AI saw a resurgence with IBM’s Deep Blue defeating chess champion Garry Kasparov (1997).
5. Modern AI Developments (2000s–Present)
Progress in machine learning, deep learning, and robotics has driven the development of AI-powered applications.:
- 2000s – AI-powered search engines (Google) and virtual assistants emerged.
- 2010s – Deep learning breakthroughs (AlphaGo defeating human champions in 2016).
- 2020s – AI-driven automation, robotics, and generative AI (like ChatGPT) revolutionized industries.
6. Founders of Artificial Intelligence
Several pioneers contributed to AI research:
- Alan Turing – Father of AI, developed the Turing Test.
- John McCarthy – Coined the term “AI” and developed Lisp programming language.
- Marvin Minsky – Co-founder of MIT AI Lab.
- Herbert Simon & Allen Newell – Developed early AI programs.
- Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, and Yoshua Bengio – Pioneers in deep learning and neural networks.
7. AI in Robotics: The Impact of AI on Modern Robotics
AI is essential in robotics, allowing robots to:
- Perceive environments using computer vision.
- Make decisions through machine learning models.
- Perform human-like tasks in healthcare, manufacturing, and space exploration.
Conclusion
The history of AI shows a fascinating journey from theoretical foundations to modern AI-powered technologies. As AI advances, its influence on shaping the future will grow even stronger. Understanding its origins helps us appreciate how far we’ve come and where AI is heading next.
References
- Britannica – Artificial Intelligence History
- Turing, Alan M. (1950). “Computing Machinery and Intelligence.” Mind.
- McCarthy, John. (1956). “Dartmouth Conference Proposal.”
- Russell, Stuart & Norvig, Peter. (2020). “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach.”

 Owner of Write Remotely. Connecting businesses with talented writers and empowering remote work.
Owner of Write Remotely. Connecting businesses with talented writers and empowering remote work.