I. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on creating machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making. With AI reshaping industries and everyday life, understanding its core concepts is essential.
In this article, we will explore the history, types, and applications of AI, as well as its subfields like Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP). We will also explore the ethical dilemmas and future impact of AI.
II. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Definition of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves creating computer systems that replicate human cognitive abilities, including learning, reasoning, and problem solving. It involves creating algorithms and models that allow machines to analyze data, make decisions, and improve over time.
Brief History of AI
| Year | Milestone | Description |
| 1950 | Turing Test | Alan Turing introduced a test to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior. |
| 1956 | Dartmouth Conference | AI became an official field of study, led by pioneers like John McCarthy. |
| 1980s | Expert Systems | AI systems were developed to mimic human decision-making in specialized fields. |
| 1997 | IBM’s Deep Blue | First AI to defeat a human chess champion (Garry Kasparov). |
| 2011 | IBM Watson | Watson won Jeopardy! against human champions. |
| 2023 | Generative AI Boom | AI models like ChatGPT and Midjourney revolutionized content creation. |
AI in Everyday Life
- Smart Assistants – Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
- Autonomous Vehicles – Tesla’s self-driving technology
- Recommendation Systems – Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon personalized recommendations
- Healthcare AI – AI-assisted medical diagnoses and robotic surgeries
III. Types of Artificial Intelligence
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
- Specializes in one specific task (e.g., voice recognition, spam filters).
- Examples: Google Search, Apple’s Siri, and AI chatbots.
2. General AI (Strong AI)
- A theoretical AI capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can.
- Not yet achieved but actively researched.
3. Superintelligence
- AI exceeding human intelligence in every aspect, raising ethical concerns and potential risks to humanity.
IV. Machine Learning Basics
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that allows machines to learn from data and enhance their performance over time.
Types of Machine Learning
| Type | Description | Example |
| Supervised Learning | Uses labeled data for training | Spam email classification |
| Unsupervised Learning | Identifies patterns in unlabeled data | Market segmentation in business |
| Reinforcement Learning | Learns through trial and error | AI playing chess or video games |
V. Deep Learning Basics
Deep Learning (DL) is an advanced form of ML that mimics the human brain using neural networks.
Neural Networks
A neural network consists of layers of interconnected nodes that process data similarly to neurons in the human brain.
Applications of Deep Learning
- Image Recognition (Google Photos, Facebook tagging)
- Autonomous Driving (Tesla, Waymo)
- Language Translation (Google Translate, DeepL)
VI. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Basics
NLP allows AI to comprehend and produce human language.
Key NLP Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| Text Analysis | Extracts meaning from text |
| Sentiment Analysis | Determines emotions in text data |
| Language Generation | AI-generated text (ChatGPT, Bard) |
Applications of NLP
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
- Sentiment analysis for social media
- Automatic translations (Google Translate)
VII. Ethical Considerations in AI
- Bias in AI algorithms – Discriminatory decision-making in hiring, lending, etc.
- Data Privacy – AI systems collect massive amounts of personal data.
- Job Displacement – AI automating human jobs in various industries.
VIII. Future of AI
- AI-powered healthcare advancements (diagnosis, drug discovery)
- AI in robotics and automation
- Ethical AI frameworks ensuring responsible AI development
IX. Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the future of technology and society. Understanding AI fundamentals, machine learning, deep learning, and NLP helps individuals stay informed in a rapidly evolving world. Whether you’re an AI enthusiast or a business professional, learning AI concepts is valuable for future innovation.
Further Learning Resources
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach – Stuart Russell & Peter Norvig
- Coursera AI & ML Courses
- Google’s AI Learning Hub
X. FAQs
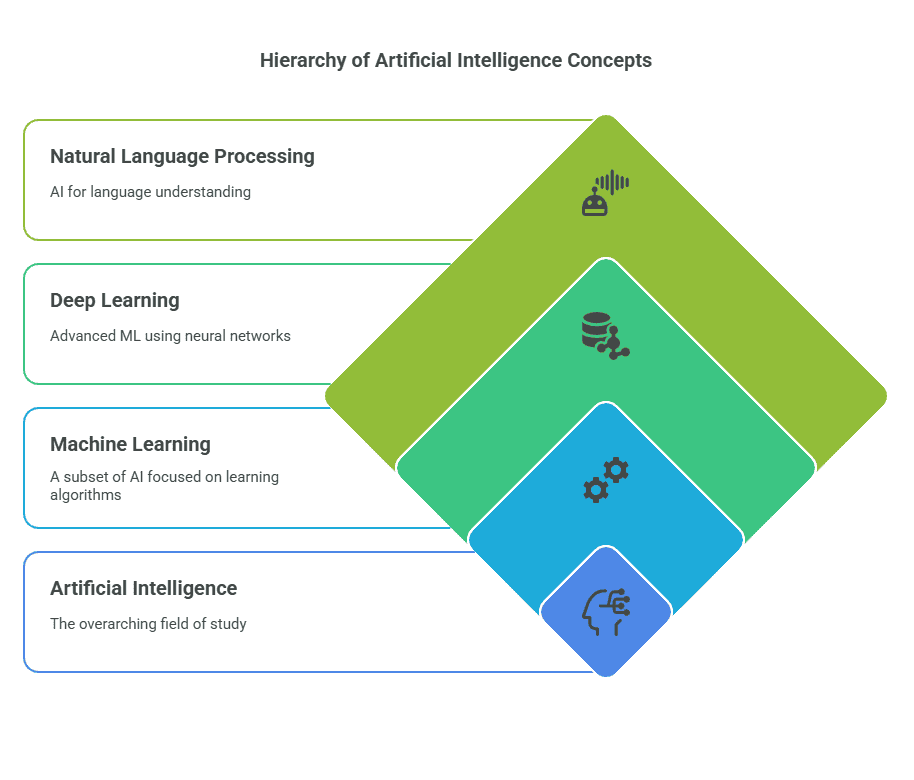
1. What is the difference between AI, ML, and DL?
- AI is the broad field of intelligent machines.
- ML is a subset of AI that learns from data.
- DL is a type of ML using neural networks.
2. Who are the pioneers of AI?
- Alan Turing, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Geoffrey Hinton are some key figures.
3. What are real-world examples of AI?
- Self-driving cars, chatbots, fraud detection, and recommendation systems.
4. How can I start learning AI?
- Enroll in online courses, read books, and practice coding in Python.
References
- Britannica – Artificial Intelligence Overview
- Russell, Stuart & Norvig, Peter. “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach.”
- Turing, Alan. “Computing Machinery and Intelligence.”

 Owner of Write Remotely. Connecting businesses with talented writers and empowering remote work.
Owner of Write Remotely. Connecting businesses with talented writers and empowering remote work.